Bone tissue augmentation in dentistry
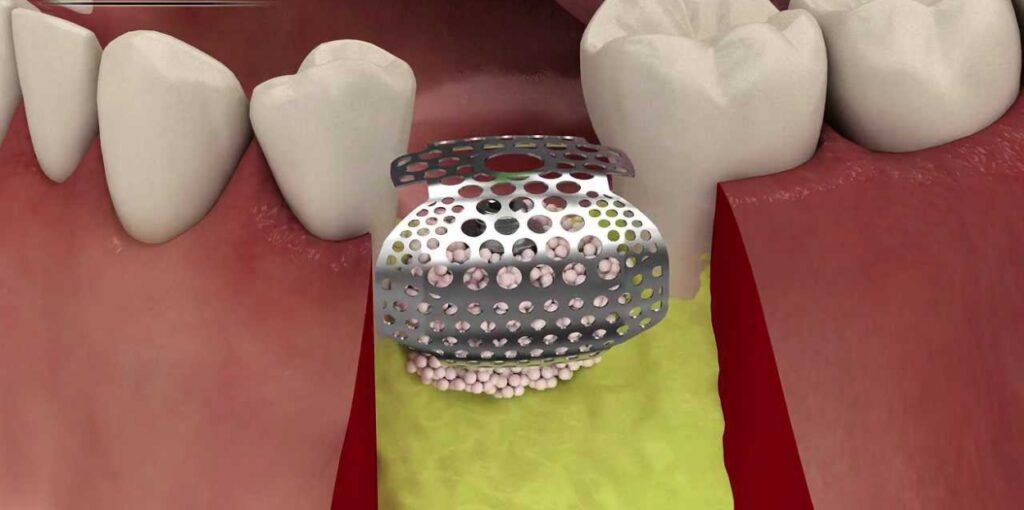
Bone tissue injury in dentistry
What is this:
Dental amputation is a procedure for restoring or replacing bone tissue in the area of teeth. These operations began in the 19th century and require a high level of professionalism and a thorough study of the patient’s medical history.
Why this is important:
A sufficient amount of bone tissue is required for a successful dental prosthesis so that the implants are well-fixed. About 2-3 months after the implantation, bone structures begin to break down, so bone strengthening becomes a necessity.
Procedure types:
- Simultaneous augmentation: Performed together with implantation if the bone tissue damage is minor. A bone replacement is used, which after 1.5 years is destroyed and replaced with its bone tissue.
- Preliminary agmentation: It is used more often when the bone tissue defect is serious. New bone tissue is formed over a long period.
Materials:
The procedures use bone tissue of animal origin, patient tissue, or artificial alloplasts.
Indications for the procedure:
A new bone tissue is formed six months after pre-augmentation, providing the following advantages:
* Proportional bones of the jaw.
* Stimulate bone growth.
* Protection against soft-tissue growth.
Output:
Its effectiveness depends on the doctor’s qualification and the patient’s compliance with all recommendations during the recovery period. Therefore, it is important to turn to experienced specialists and follow their recommendations on time.